Mental Health Issues
Consult Best Psychologist in Gurgaon and Delhi NCR for any Mental Health or Relationship Concerns.
If you or your dear ones have been diagnosed or suspecting any kind of Mental health issue or distress, consult Smile Spreaders, Best Platform for all your Mental Health Needs.
We help in diagnosing and treatment of the above conditions through designing individualized therapeutic plans.
We cater to different kinds of mental health issues, some of which are depression, anxiety, loneliness, grief, relationship issues, loneliness, low self-esteem, low confidence, panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, separation anxiety, selective mutism, social phobia, specific phobia, anxiety due to a medical condition, OCD, Adjustment Disorder, Post Traumatic Stress Disorder, Personality Disorders, addictions, attention deficit hyper active disorder (ADHD), Autism, Mental Retardation, Specific Learning Disability, Dementia, Alzheimer’s and other emotional and behavioural disorders in all age groups.
DEPRESSION
The 3 common symptoms of depression are depressed mood, loss of interest and enjoyment, and reduced energy leading to increasedfatiguability anddiminished activity. If you are suffering from any of these symptoms,persisting more than 2 weeks, visiting a psychologist is highly recommended.



ANXIETY
Experiencing occasional anxiety is a normal part of life. However, people with anxiety disorders frequently have intense, excessive and persistent worry and fear about everyday situations. These feelings of anxiety and panic interfere with daily activities, are difficult to control, are out of proportion to the actual danger and can last a long time. You may avoid places or situations to prevent these feelings.
- Anxiety disorder due to a medical condition includes symptoms of intense anxiety or panic that are directly caused by a physical health problem.
- Generalized anxiety disorder includes persistent and excessive anxiety and worry about activities or events — even ordinary, routine issues. The worry is out of proportion to the actual circumstance, is difficult to control and affects how you feel physically. It often occurs along with other anxiety disorders or depression.
- Selective mutism is a consistent failure of children to speak in certain situations, such as school, even when they can speak in other situations, such as at home with close family members. This can interfere with school, work and social functioning.
- Separation anxiety disorder is a childhood disorder characterized by anxiety that's excessive for the child's developmental level and related to separation from parents or others who have parental roles.
- Social anxiety disorder (social phobia) involves high levels of anxiety, fear and avoidance of social situations due to feelings of embarrassment, self-consciousness and concern about being judged or viewed negatively by others.
- Specific phobias are characterized by major anxiety when you're exposed to a specific object or situation and a desire to avoid it. Phobias provoke panic attacks in some people.
OBSESSIVE-COMPULSIVE DISORDER
Obsessional thoughts are ideas, images or impulses that enter theindividual's mind again and again in a stereotyped form. They are almost invariablydistressing (because they are violent or obscene, or simply because they are perceived assenseless) and the sufferer often tries, unsuccessfully, to resist them.Compulsive acts or rituals are stereotyped behaviours that are repeated again andagain. They are not inherently enjoyable, nor do they result in the completion of inherentlyuseful tasks. The individual often views them as preventing some objectively unlikely event,often involving harm to or caused by himself or herself.
If the symptoms are present on mostdays for at least 2 successive weeks and be a source of distress or interference with activities, you must consult psychologist.
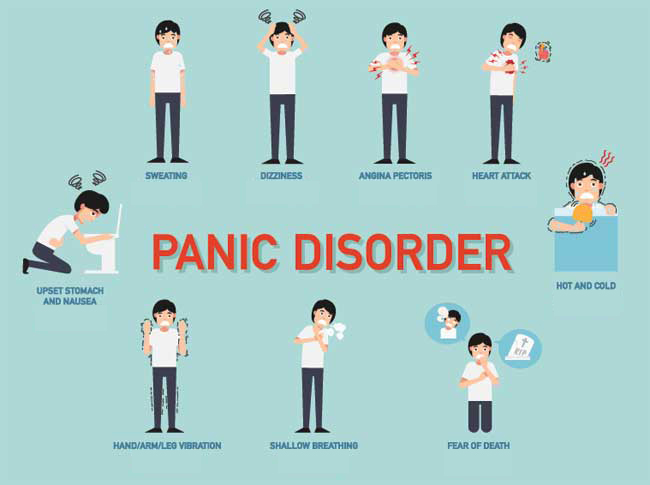
PANIC DISORDER
Essential features are recurrent attacks of severe anxiety (panic) which are not restricted to anyparticular situation or set of circumstances, and which are therefore unpredictable.Suddenonset of palpitations, chest pain, choking sensations, dizziness, and feelings of unrealityare common. There is also, almost invariably, asecondary fear of dying, losing control, or going mad. Individual attacks usually last forminutes only, though sometimes longer; their frequency and the course of the disorder areboth rather variable. This requires consultation with a psychologist.
ADJUSTMENT DISORDER
States of subjective distress and emotional disturbance, usually interfering with social functioning andperformance, and arising in the period of adaptation to a significant life change or to theconsequences of a stressful life event (including the presence or possibility of serious physicalillness).The onset is usually within 1 month of the occurrence of the stressful event or life change and has not exceeded 6 months, shall consult a psychologist for better coping and self-regulation.

PSYCHO-SOMATIC ISSUES
Psychosomatic disorder is a psychological condition involving the occurrence of physical symptoms, usually lacking a medical explanation. People with this condition may have excessive thoughts, feelings or concerns about the symptoms — which affects their ability to function well. Psychological Assessment and Therapy can help and is highly recommended.
LOW SELF ESTEEM/ CONFIDENCE
Low self-esteem is when someone lacks confidence about who they are and what they cando. They often feel incompetent, unloved, or inadequate. People who struggle with low self-esteem are consistently afraid about making mistakes or letting other people down. Psychotherapy can greatly help individuals feeling lack in self-abilities and make them reach to their highest potential.


RELATIONSHIP ISSUES
Common relationship challenges may include infidelity, loss of intimacy, communication difficulties, coping with stress challenges, financial pressures, boundary violations, difficulty balancing individual and couple expectations, divorce, separation and breaking up. Therapy can greatly help you give self-insights and ways of better coping, along with answering the questions in your mind related to your experiences.
PERSONALITY DISORDERS
These types of condition comprise deeply ingrained and enduring behaviourpatterns, manifesting themselves as inflexible responses to a broad range ofpersonal and social situations. They represent either extreme or significantdeviations from the way the average individual in a given culture perceives,thinks, feels, and particularly relates to others. Such behaviour patterns tend to bestable and to encompass multiple domains of behaviour and psychologicalfunctioning. They are frequently, but not always, associated with various degreesof subjective distress and problems in social functioning and performance.
Different types of therapies are suggested for various personality disorders, which are immensely helpful for an improved socio emotional wellbeing.


Bipolar Mood (or Affective) Disorder
This disorder, earlier known as manic depressive psychosis(MDP), is characterised by recurrent episodesof mania and depression in the same patient at differenttimes.
These episodes can occur in any sequence. Thepatients with recurrent episodes of mania (unipolarmania) are also classified here as they are rare andoften resemble the bipolar patients in their clinicalfeatures.
ADDICTIONS
SUBSTANCE ADDICTION
A definite diagnosis of dependence should usually be made only if three or more of the following have been present together at some time during the previous year:
- A strong desire or sense of compulsion to take the substance;
- Difficulties in controlling substance-taking behaviour in terms of its onset, termination, or levels of use;
- A physiological withdrawal state when substance use has ceased or been reduced, as evidenced by: the characteristic withdrawal syndrome for the substance; or use of the same (or a closely related) substance with the intention of relieving or avoiding withdrawal symptoms;
- Evidence of tolerance, such that increased doses of the psychoactive substances are required in order to achieve effects originally produced by lower doses (clear examples of this are found in alcohol- and opiate-dependent individuals who may take daily doses sufficient to incapacitate or kill nontolerant users);
- progressive neglect of alternative pleasures or interests because of psychoactive substance use, increased amount of time necessary to obtain or take the substance or to recover from its effects;
- persisting with substance use despite clear evidence of overtly harmful consequences, such as harm to the liver through excessive drinking, depressive mood states consequent to periods of heavy substance use, or drug-related impairment of cognitive functioning; efforts should be made to determine that the user was actually, or could be expected to be, aware of the nature and extent of the harm.
There are various other types of addictions that exists apart from stances, like gaming, mobile addictions, porn watching, tea/coffee addiction etc.


DEMENTIA
Dementia is a syndrome due to disease of the brain, usually of a chronic or progressive nature, in which there is disturbance of multiple higher cortical functions, including memory, thinking, orientation, comprehension, calculation, learning capacity, language, and judgement. Consciousness is not clouded. Impairments of cognitive function are commonly accompanied, and occasionally preceded, by deterioration in emotional control, social behaviour, or motivation.
This syndrome occurs in Alzheimer's disease, in cerebrovascular disease, and in other conditions primarily or secondarily affecting the brain.Dementia produces an appreciable decline in intellectual functioning, and usuallysome interference with personal activities of daily living, such as washing, dressing,eating, personal hygiene, excretory and toilet activities.
SCHIZOPHRENIA
The schizophrenic disorders are characterized in general by fundamental and characteristic distortions of thinking and perception, and affects that are inappropriate or blunted. Clear consciousness and intellectual capacity are usually maintained although certain cognitive deficits may evolve in the course of time.
The most important psychopathological phenomena include thought echo; thought insertion or withdrawal; thought broadcasting; delusional perception and delusions of control; influence or passivity; hallucinatory voices commenting or discussing the patient in the third person; thought disorders and negative symptoms.

